Details
Population Reference Bureau (2021)
FAMILY PLANNING POLICY ENVIRONMENTS
20 Essential Resources
Details
Family Planning and Reproductive Health Indicators Database
Family planning policy environments are made up of a set of government, organizational, and community commitments, frameworks, strategies, regulations, and guidelines. Policies help determine contraceptive availability, demand, access, and use—influencing options and opportunities for the nearly two billion women and girls of reproductive age around the world. The policy environment within which all family planning programming (private or public) occurs is complex and multifaceted. Enabling aspects of a policy environment can support access to and use of family planning resources, while restrictive aspects inhibit access to and use of family planning resources for certain groups of people or in certain situations.
Many factors shape policy environments, including available evidence, institutional capacity, social norms, political dynamics, public opinion, and global frameworks and guidelines.
This collection of essential resources is for family planning program planners, implementers, decision-makers, and advocates who work within and seek to understand and influence family planning policy environments. The collection provides tools to measure and/or assess policy environments, approaches that explain how to influence family planning policy environments, overviews of policy environments, and resources to enable a better understanding of key policy topics.

Publication

Webpage
Map
Data for Impact (2017)
Youth Family Planning Policy Scorecard
Details
Demographic Dividend Effort Index Launch Webinar
Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health (2021)
Details
National Composite Index on Family Planning
Track20 (2017)
Curated by
KNOWLEDGE SUCCESS & PRB
How to use this collection
Details
Measurement and Asssessment Tools Influencing Policy Environments Policy Environment Overviews Policy Resources on Key Topics
Icons demonstrate the resource format.
Details
Details
Measurement and Assessment Tools
Details
Contributors
Design: Emily Haynes
Writers: Shelley Megquier and Kaitlyn Patierno
Technical input and review: Natalie Apcar, Alison Bodenheimer, Brittany Goetsch, and Sarah Harlan
About Knowledge SUCCESS
Knowledge SUCCESS (Strengthening Use, Capacity, Collaboration, Exchange, Synthesis, and Sharing) is a five-year (2019-2024) global project led by a consortium of partners and funded by USAID’s Office of Population and Reproductive Health to support learning, and create opportunities for collaboration and knowledge exchange, within the family planning and reproductive health community. We use an intentional and systematic approach, called knowledge management, to help programs and organizations working in family planning and reproductive health collect knowledge and information, organize it, connect others to it, and make it easier for people to use.
About Population Reference Bureau (PRB)
PRB is a nonpartisan research organization focused on improving the health and well-being of people globally through evidence-based policies and practices.












This collection was curated and published in September 2021. Resource links were active at the date of publication. Images courtesy of DFID Flickr, Images of Empowerment, USAID Flickr, and World Bank Photo Collection Flickr.
Acknowledgements

This collection is made possible is made possible by the support of the American People through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) under the Knowledge SUCCESS (Strengthening Use, Capacity, Collaboration, Exchange, Synthesis, and Sharing) Project. Knowledge SUCCESS is supported by USAID’s Bureau for Global Health, Office of Population and Reproductive Health and led by the Johns Hopkins Center for Communication Programs (CCP) in partnership with Amref Health Africa, The Busara Center for Behavioral Economics (Busara), and FHI 360. The contents of this webpage are the sole responsibility of CCP. The information provided on this webpage does not necessarily reflect the views of USAID, the United States Government, or the Johns Hopkins University.



Icons demonstrate the resource format.
Measurement and Assessment Tools
Measurement and Assessment Tools
Measurement and Assessment Tools
Details
Health Policy Plus and Knowledge for Health (2018)
Costed Implementation Plans for Family Planning

Details
Details
Commit to FP2030 Toolkit
FP2030 (2021)
Details
Details
The Four Dividends
Population Reference Bureau (2021)
Details
Details
Details
Details
World Health Organization (2021)
Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights Policy Portal
Details
Details
Policy Communication Toolkit
Details
Details
Advance Family Planning Advocacy Portfolio
Details
Details
Adding It Up: Investing in Sexual and Reproductive Health
Guttmacher Institute (2020)
Details
Details
Knowledge SUCCESS (2021)
Adolescent Responsive Health Systems Recap
Details
Details
Advocacy for Self-Care in Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights
Advance Family Planning (2021)

Details
Details
A Rapid Review of Task-Sharing Policies
BMC (2021)

Details
Details

Details
Details
Health Policy Plus (2020)
Fostering Joint Accountability Within Health Systems
Details
Details
Details
Details
Best Practices in Sustaining Youth Contraceptive Use
Population Reference Bureau (2021)

Details
Details
Effects of COVID-19 on FP/RH Care and Emerging Adaptations
MOMENTUM Knowledge Accelerator (2020)
Details

Video
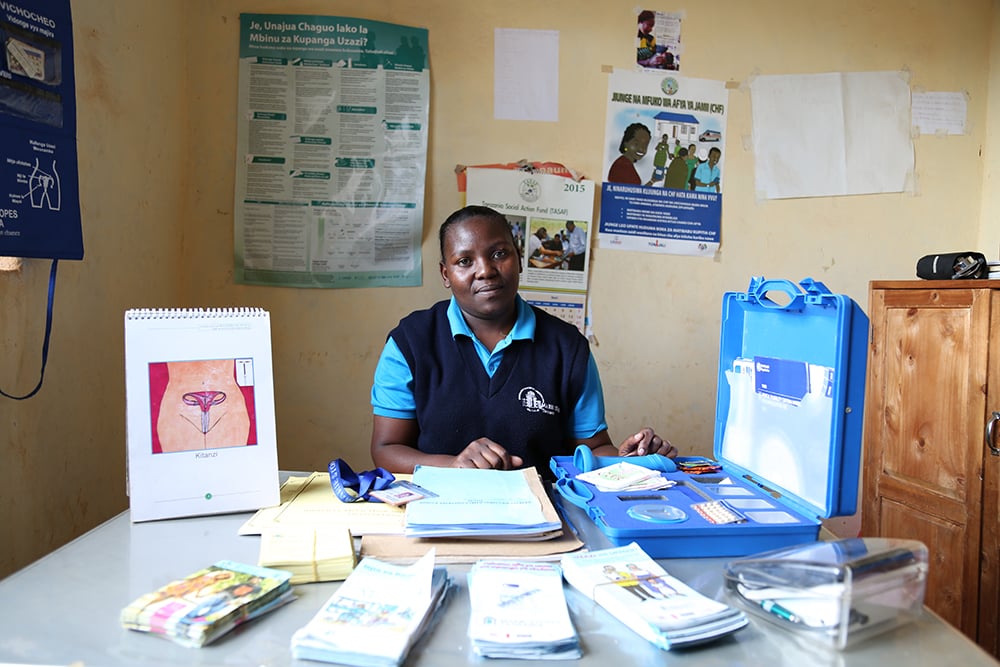
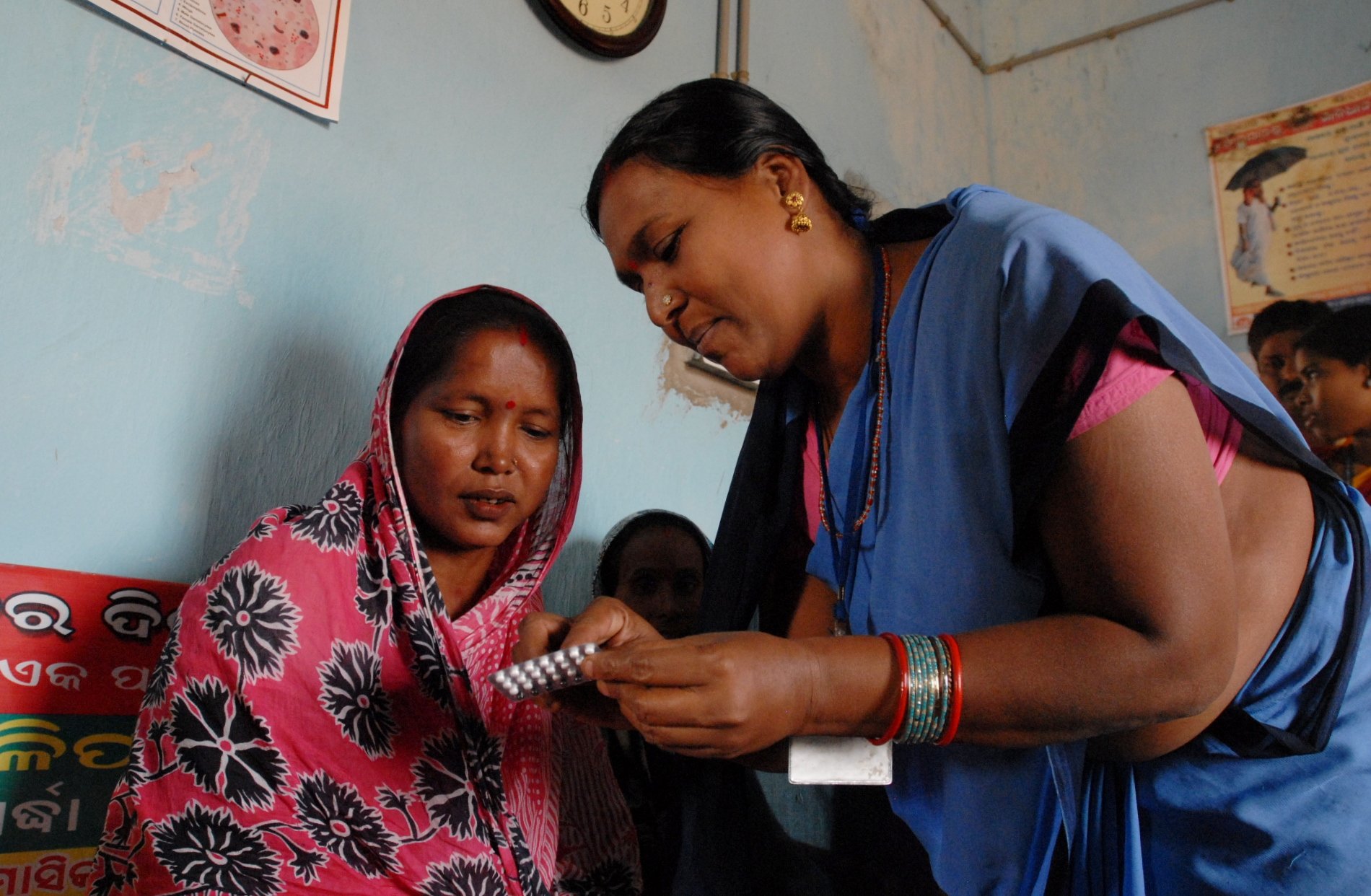
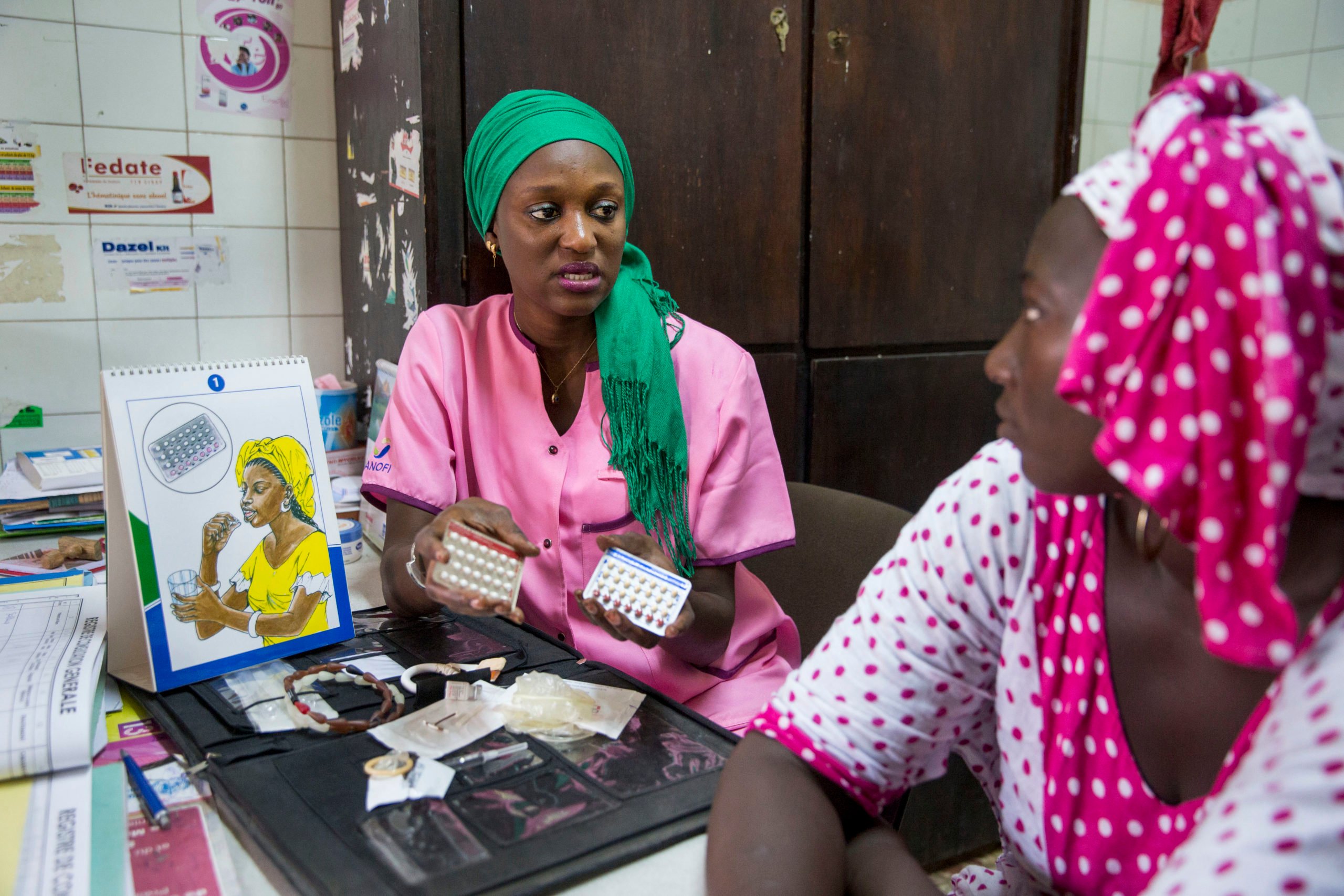
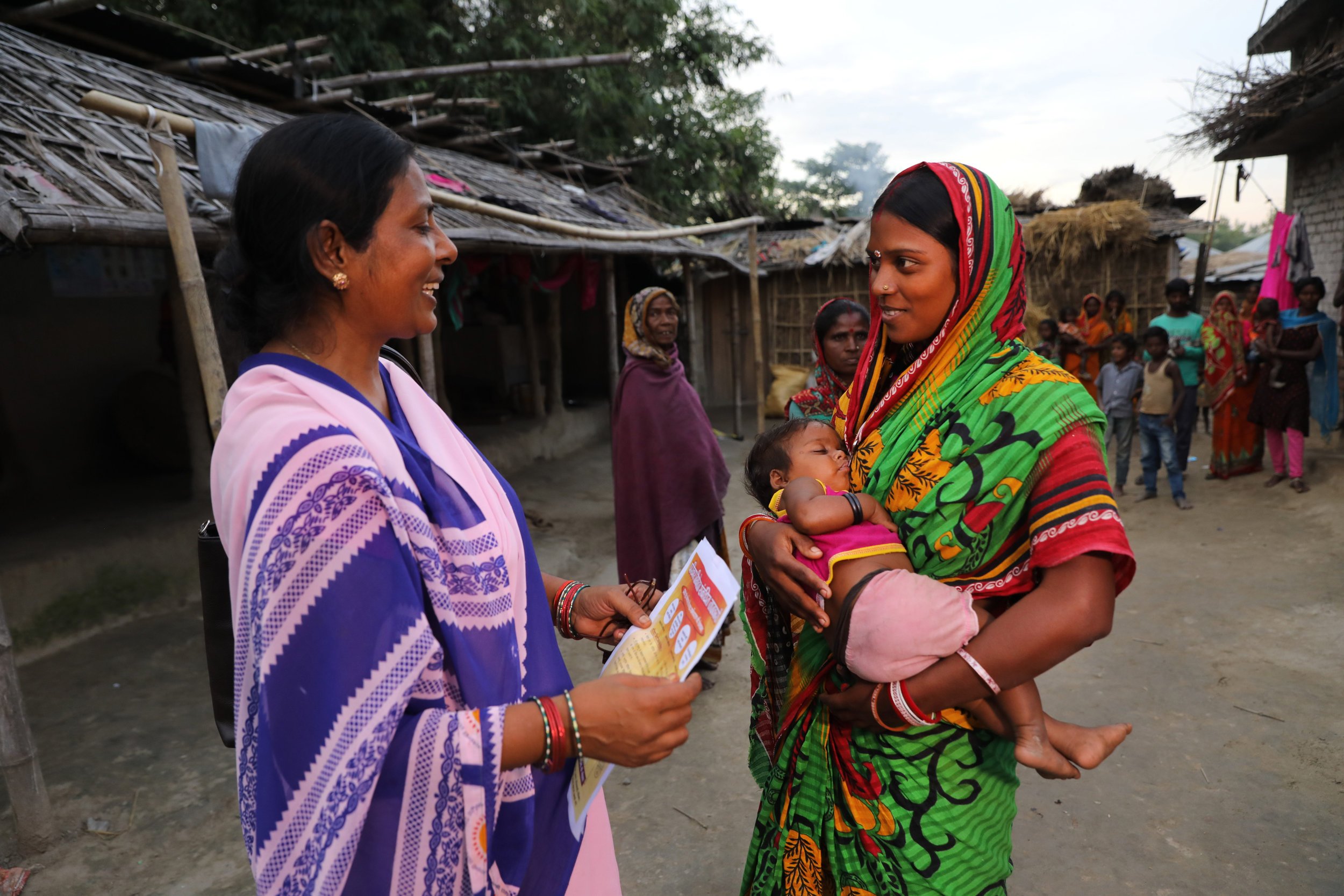
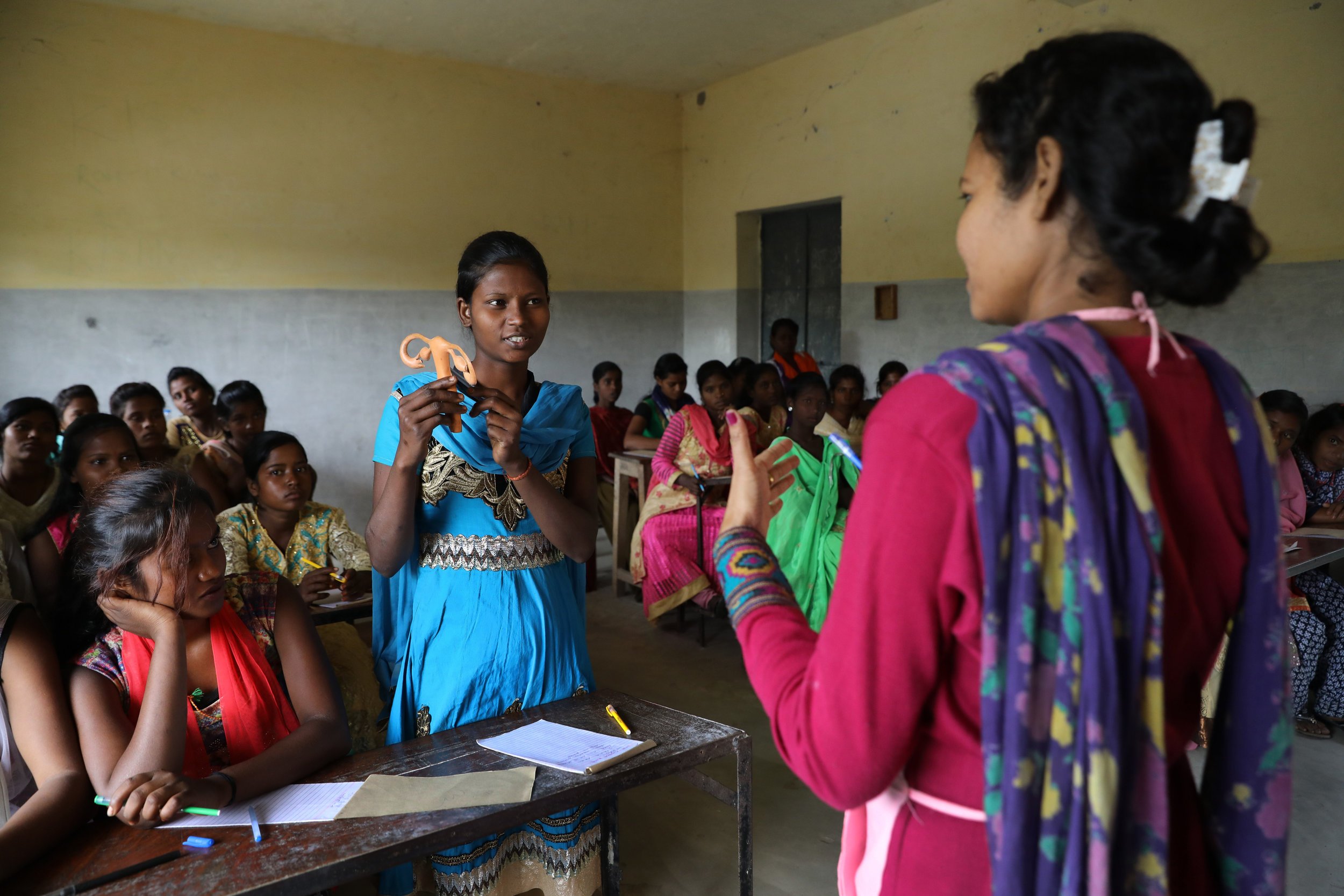
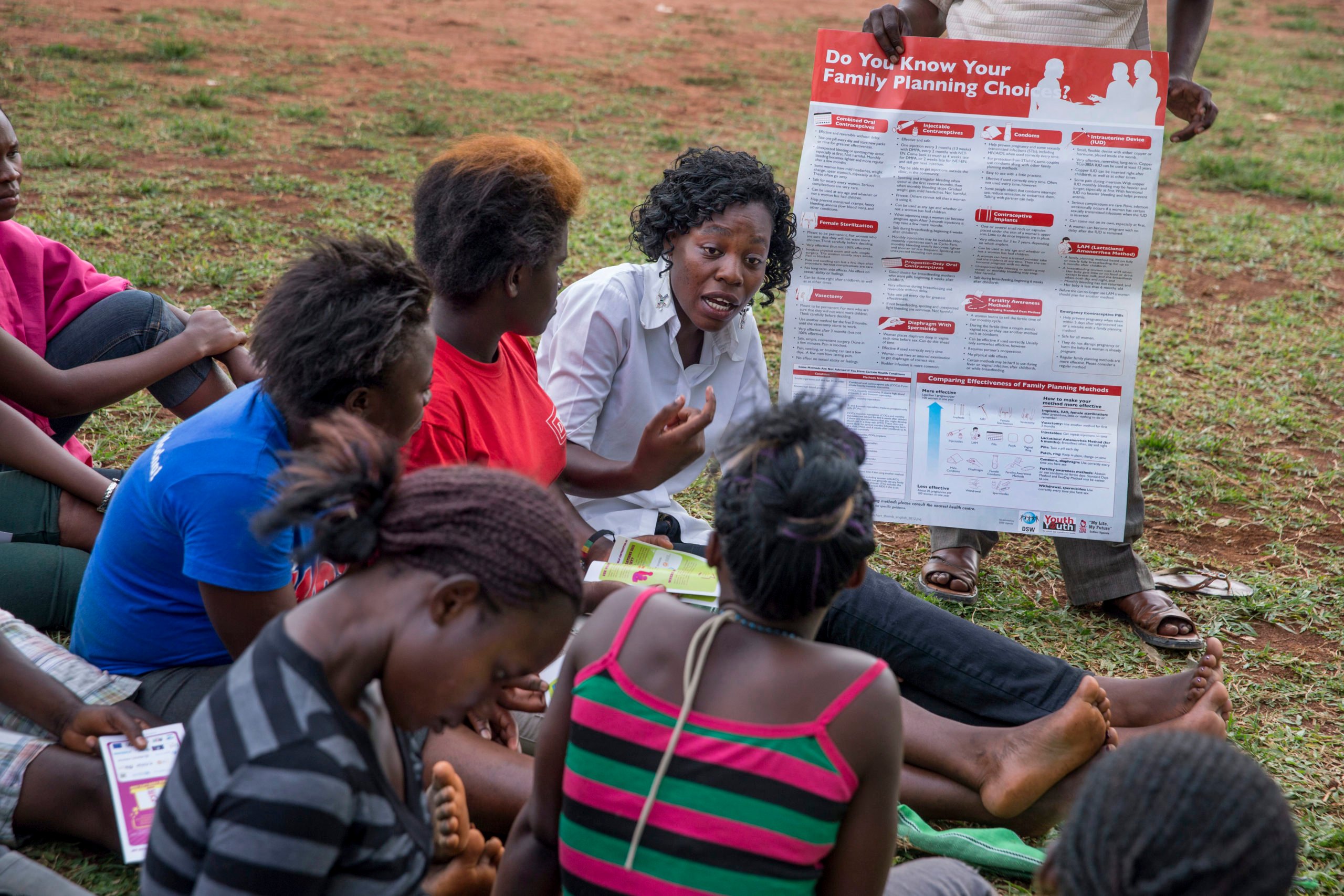
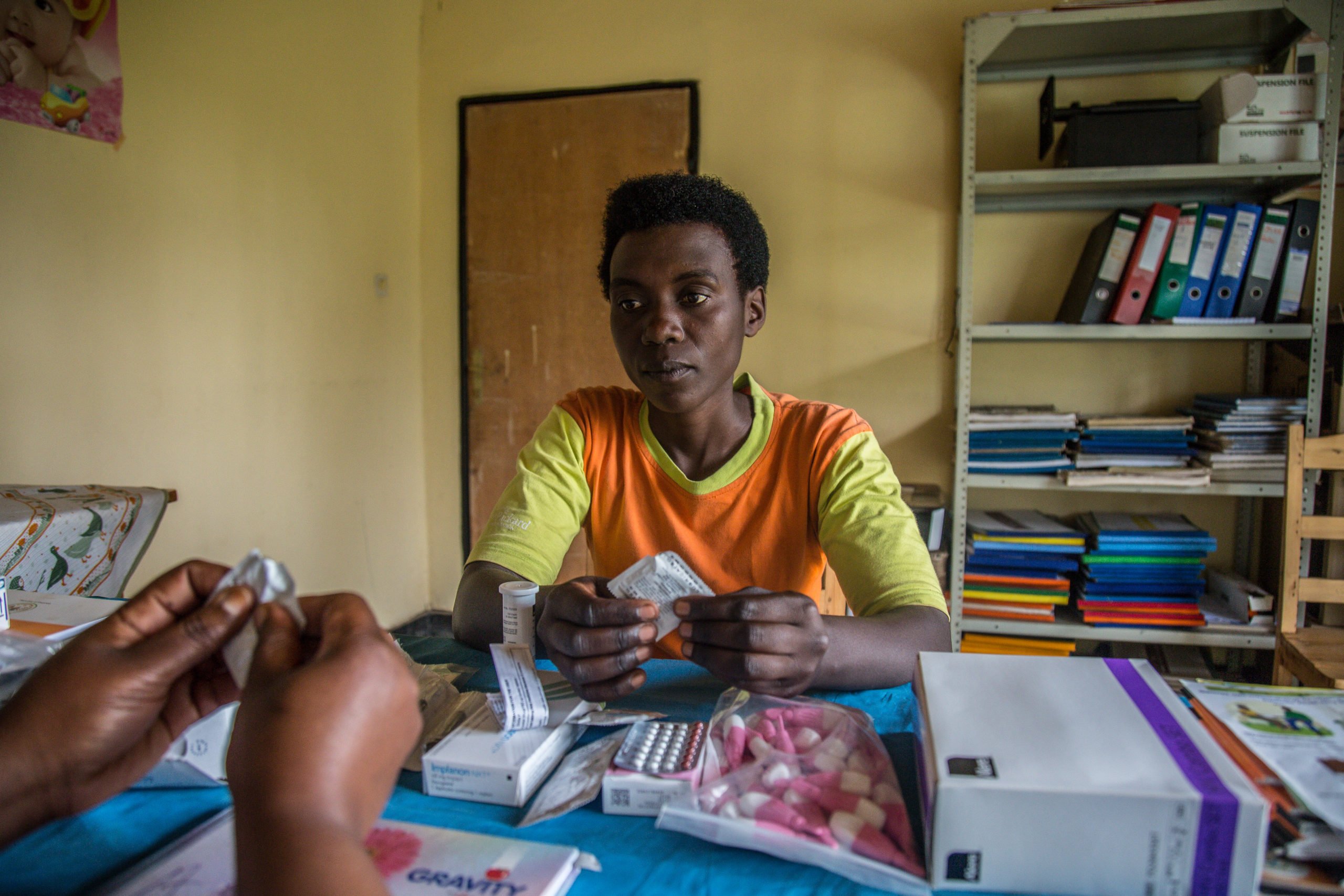













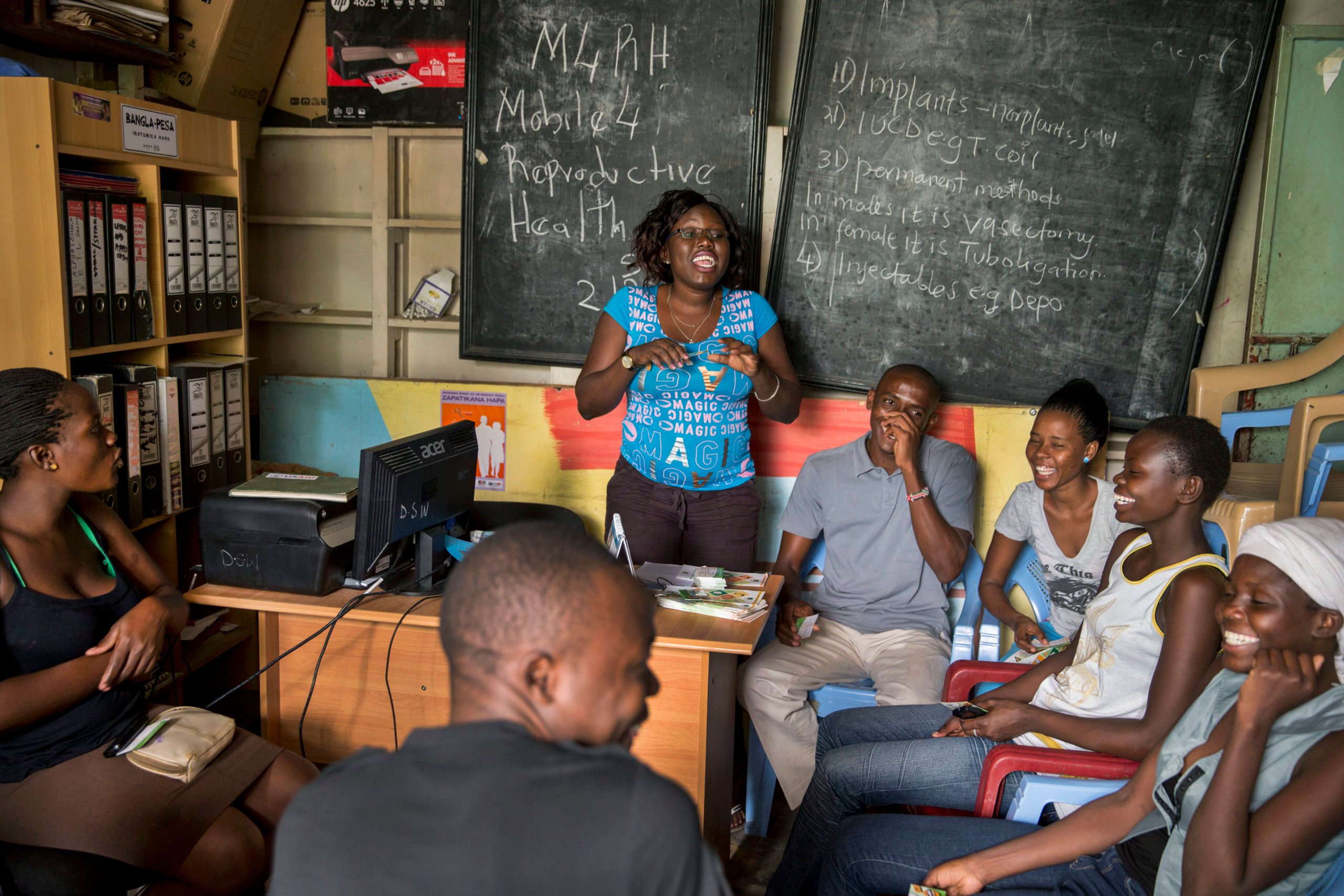



Initially developed by PRB in 2017 and updated annually since then, the Youth Family Planning Policy Scorecard evaluates and compares the favorability of current national policy and program environments. Based on research and analysis of the most effective policies and program interventions, it promotes the uptake of contraception among youth ages 15–24.
A digital platform allows users to access, interpret, and compare 28 countries’ youth family planning policies and programming to see the extent to which a country’s policy environment enables and supports youth access to and use of family planning. Digital platform and print versions are available in French and English.
About PRB
PRB is a nonpartisan research organization focused on improving the health and well-being of people globally through evidence-based policies and practices.
Get The Resource
The Youth FP Policy Scorecard compiles evidence and analysis on effective policy and program interventions in one place, making information easily digestible and accessible to decision-makers. It provides measurable guidance to governments and other stakeholders on youth family planning.
Population Reference Bureau (2021)
Youth Family Planning Policy Scorecard
Why is it essential?



Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Policy development and implementation is a complex process involving numerous stakeholders, which can create unique challenges for monitoring and evaluation. Nonetheless, it is important to generate rigorous learning about how policies are generated and implemented and what impact they ultimately have. The Family Planning and Reproductive Health Indicators Database includes a number of policy-relevant indicators that can be used to evaluate investments to generate political and financial commitment to family planning across various contexts.

The Family Planning and Reproductive Health Indicators Database provides a comprehensive listing of the most widely used indicators for evaluating FP/RH programs worldwide. Updated periodically since 2012, the menu of indicators included in the database can be used in monitoring and evaluation of programs that aim to strengthen health-seeking behaviors, service delivery, and an enabling environment for family planning. Within the Family Planning programmatic area, the subarea on Repositioning Family Planning includes a number of indicators pertaining to policy development, policy implementation, and resource mobilization. Within the Health Systems programmatic area, the subarea on Policy Environment provides illustrative policy indicators that can be tailored, modified, or expanded based on the local context within which they are applied.
About Data for Impact
Data for Impact (D4I), a project funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), uses innovative methods to generate strong evidence for program and policy decision making. The project works with countries to increase local organizational and technical capacity and prepare country partners to independently conduct evaluations, analyze data, and use evidence to inform program and policy decisions.
Data for Impact (2017)
Family Planning and Reproductive Health Indicators Database

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
The DDEI takes researchers, policymakers, advocates, service providers, and program implementers through a webinar that highlights how the DDEI can be used to foster measurement, dialogue across sectors, and innovation in six key sectors: family planning, maternal and child health, education, women’s empowerment, labor market, and governance and economic institutions.

The demographic dividend is the accelerated economic growth that can result from improved reproductive health, a rapid decline in fertility, and the subsequent shift in population age structure. Over the last decade, many African Union member states have instituted national demographic dividend roadmaps. To support performance assessment, documentation of best practices, and knowledge sharing around approaches to harness the demographic dividend, the Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health collaborated with national and regional partners in six countries to develop the Demographic Dividend Effort Index (DDEI) tool. Collaborating partners include the Centre d’Excellence Régional en Économie Générationnelle in Senegal, the Center for Communication Programs in Nigeria, the National Council for Population and Development in Kenya, the Tanzania Communication and Development Center, the Ethiopian Academy of Sciences, and the Centre for Integrated Development Research and Action in Rwanda.
On World Population Day 2021, the Gates Institute launched the DDEI in collaboration with a panel of regional and local civil society partners. The webinar highlights findings and lessons learned from the six pilot countries.
About Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health
The Gates Institute is located within the Department of Population, Family, and Reproductive Health at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. It conducts and facilitates cutting-edge research in family planning, reproductive health, and population dynamics and translates science into evidence-informed policies, programs, and practice.
Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health (2021)
Demographic Dividend Effort Index Launch Webinar

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Standardizing measures to allow for comparability across countries can support an understanding of comparable strengths and weaknesses across family planning policy environments and allow decision-makers and advocates to prioritize their efforts.

First undertaken in 2014 and last updated in 2017, the index builds on the long-standing National Family Planning Effort Index. The data are intended for policy and planning use by family planning stakeholders.
The index supports efforts to strengthen the enabling environment for family planning across FP2020 countries. This resource measures both the existence of family planning policies and program implementation, compiling data into 35 scores across five dimensions of an enabling environment.
About Track20
Through the Track20 Project, implemented by Avenir Health, progress was monitored toward achieving the goals of the global FP2020 initiative, working directly with governments in participating countries.
Track20 (2017)
National Composite Index on Family Planning

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
The portal allows users to track a country’s progress in adopting World Health Organization recommendations on policies, strategies, and guidelines and enables countries to research and adopt evidence-based policies in their own settings.

The Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights Policy Portal contains country profiles that are based on gathered responses to the Global Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child, and Adolescent Health Policy Survey conducted in 2018/2019. World Health Organization country offices coordinated the completion of the survey with the Ministry of Health and other UN partners.
The policy portal shares information from 155 countries across six components of sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR): sexual health, infertility, sexually transmitted infections, family planning, cervical cancer, and violence against women. The family planning section of the policy portal includes 22 indicators that can be used for assessing a policy environment.
About the World Health Organization
Dedicated to the well-being of all people and guided by science, the World Health Organization leads and champions global efforts to give everyone, everywhere an equal chance to live a healthy life.
World Health Organization (2021)
Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights Policy Portal

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Research often has profound implications for policy, but without effective communication and engagement between researchers and policy audiences, the significance of research findings may be lost. Through this toolkit, users can build skills to bridge this gap, with the goal of increasing the use of evidence in policy and program decision-making.

This Policy Communication Toolkit is a resource to bridge the gap that often lies between research and policy. It consolidates tools, materials, and approaches PRB has developed and refined over 30 years of training researchers to communicate with policy audiences. This training toolkit can be used to help researchers and advocates understand the process by which research informs the policy environment; identify key policy audiences; identify and communicate the policy implications of research; and communicate messages through a variety of platforms, including policy briefs, oral presentations, data visualizations, social media, and more. The toolkit is available in English, French, and Spanish.
About the Population Reference Bureau (PRB)
PRB is a nonpartisan research organization focused on improving the health and well-being of people globally through evidence-based policies and practices.
Population Reference Bureau (2018)
Policy Communication Toolkit

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Policymakers and other decision-makers often request pragmatic data on the costs and impacts of different interventions including family planning. This widely-cited resource provides critical information on cost savings associated with investment in sexual and reproductive health, making it a “go-to” for advocates, implementers, and policymakers alike.

Produced by the Guttmacher Institute since 2003, Adding It Up provides estimates of the costs and impact of providing essential family planning and reproductive health services to all women of reproductive age (15–49), as well as adolescents, in low- and middle-income countries. Aimed at national and local governments, the private sector, and international development partners, the report aims to highlight the magnitude of investments needed as well as the returns on these investments for individuals, communities, and nations. The associated country profiles provide data and resources for each of the 132 countries included in the study.
About Guttmacher Institute
The Guttmacher Institute is a leading research and policy organization committed to advancing sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) worldwide.
Adding It Up: Investing in Sexual and Reproductive Health

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
The advocacy portfolio offers in-depth guidance on how family planning champions can influence policy environments for measurable and lasting change.

This resource provides a step-by-step guide to developing and implementing a SMART—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound—advocacy approach that focuses on opportunities that have the highest potential for success in the near term. It connects short-term advocacy strategies and wins with broad, long-term goals.
As a collection of advocacy best practices and tools, the Advance Family Planning Advocacy Portfolio helps family planning advocates develop strategic plans to achieve their desired results. Available in English and French, the portfolio includes guides, worksheets, and presentations on developing a family planning advocacy strategy, implementing a plan, and capturing results.
About Advance Family Planning
The Advance Family Planning initiative was launched in 2009 at the Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health within the Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Advance Family Planning (2017)
Advance Family Planning Advocacy Portfolio

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
The toolkit offers step-by-step guidance to commitment-making for governments and other stakeholders with a strong focus on rights-based approaches and accountability mechanisms.

FP2030 is a new partnership built on the foundation of FP2020. The Commit to FP2030 Toolkit provides guidance for country partners who are poised to make a new or renewed commitment to advancing family planning.
The toolkit includes suggested commitment-making processes that can be adapted to fit unique country contexts, commitment forms, guiding principles, and a multitude of resources for governments and other stakeholders. Thematic resources are also available within the toolkit on topics like adolescents and youth, emergency preparedness, financing, method choice, and other topics. The toolkit is available in French and English.
About FP2030
FP2030 is a global partnership that envisions a future where women and girls everywhere have the freedom and ability to lead healthy lives, make their own informed decisions about using contraception and having children, and participate as equals in society and its development. FP2030 has a strong focus on country leadership and deep partnerships with civil society, including youth-led organizations and associations. It is driven by the power of commitments and globally shared goals and grounded in a rights-based, equity-focused vision that goes beyond the numbers.
FP2030 (2021)
Commit to FP2030 Toolkit

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Costed implementation plans (or CIPs) are important policy documents that establish multi-year plans for achieving family planning priorities and costed implementation strategies.

This guide is an update of the 2015 Costed Implementation Plans (CIP) for Family Planning: 10-Step Process for CIP Planning, Development, and Execution. The primary users of this tool are CIP’s Ministry of Health focal points, project managers, monitoring and evaluation officers, technical support teams, and task forces; national family planning technical working groups; CIP strategic advisory groups; FP2020; the Ouagadougou Partnership Coordination Unit; and others.
This practical guide outlines and summarizes a series of steps, activities, and tools involved in planning, developing, and executing a CIP. It includes links to CIP tools and resources for users to access throughout the steps.
About Health Policy Plus
Health Policy Plus (HP+) is a seven-year cooperative agreement funded by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), beginning August 28, 2015. HP+ strengthens and advances health policy priorities at global, national, and subnational levels.
About Knowledge for Health
Knowledge for Health (K4Health) was the flagship knowledge management project of USAID from 2013–2019. K4Health collected, curated, and adapted the latest evidence and best practices on family planning, reproductive health, and other global health areas.
Health Policy Plus and Knowledge for Health (2018)
Costed Implementation Plans for Family Planning: 10-Step Process for CIP Planning, Development, and Execution

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Access to and use of voluntary family planning can contribute to age-structure change, which delivers benefits across different facets of society. This resource can help advocates demonstrate the benefits of investment in family planning goals across policy sectors, inspiring policymakers to make strong commitments to family planning and reproductive health.

The demographic dividend is commonly defined as the accelerated economic growth that can occur as a population age structure matures. Initially developed by PRB through the USAID-funded PACE Project in 2018, the Four Dividends web feature expands the concept of the demographic dividend to four potential sets of benefits, or dividends. In addition to economic growth, it outlines benefits in health, education, and governance and stability. This resource explains how reaching important benchmarks under each of these dividends becomes more likely as countries progress through the demographic transition from high fertility to low fertility. With a better understanding of the potential benefits of age structure change across key development sectors, policymakers can effectively channel investments in family planning and other programs to promote a demographic transition and achieve the four dividends.
About Population Reference Bureau (PRB)
PRB is a nonpartisan research organization focused on improving the health and well-being of people globally through evidence-based policies and practices.
Population Reference Bureau (2021)
The Four Dividends

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Pronounced disparities between the laudable goals of family planning policies and on-the-ground realities are common. By expanding spaces for dialogue and negotiation, accountability initiatives can shrink the discrepancy between political aspirations and lived realities.

As Family Planning 2020 transitions into the Family Planning 2030 (FP2030) partnership, many countries are recommitting to advancing rights-based family planning programs that improve the lives of their population, especially women and girls. The commitment-making process requires a mutual accountability approach, where governments, in collaboration with key stakeholders, are held to account for commitments they make, and civil society has the knowledge, tools, and resources to monitor progress toward those commitments.
This guide is a roadmap that advocates, program implementers, and decision-makers can use to increase knowledge of accountability within health systems, gain skills to better understand existing accountability linkages, and seek consensus-driven recommendations for action.
About Health Policy Plus
Health Policy Plus is a USAID-funded project that aims to strengthen and advance health policy priorities at global, national, and subnational levels. The project is a partnership between Palladium, Avenir Health, Futures Group Global Outreach, Plan International USA, Population Reference Bureau, RTI International, the White Ribbon Alliance for Safe Motherhood, and ThinkWell.
Health Policy Plus (2020)
Fostering Joint Accountability Within Health Systems: A Guide for Engaging Local Leaders as Champions

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
There are six established Enabling Environment HIPs that describe evidence-based approaches for addressing social, financial, and political barriers to family planning information and services. Use of these proven approaches can strengthen family planning policy environments across a broad range of settings.

The family planning High Impact Practices (HIPs) identify and describe approaches proven to increase contraceptive use in a wide range of countries in easily digestible briefs and newly added PowerPoint presentations. HIPs are identified based on the demonstrated magnitude of impact on contraceptive use and potential application in a wide range of settings.
HIPs are categorized as either supporting enabling environments, service delivery, social and behavior change, or as HIP enhancements. This seminal two-page brief provides a list of all the HIPs identified by the Technical Advisory Group and is available in English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish.
About the High Impact Practices Partnership
The High Impact Practices in Family Planning (HIPs) are a set of evidence-based family planning practices vetted by experts against specific criteria and documented in an easy-to-use format. The partnership is supported by over 60 organizations that play a vital role in developing, reviewing, disseminating, and implementing HIPs in family planning programs.
The High Impact Practices Partnership (2019)
Family Planning High Impact Practices

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
UHC means all people have access to the quality health services they need, without suffering financial hardship. However, family planning is not always considered in the design, introduction, or scale-up of UHC mechanisms such as health insurance. The guide can help to determine what policy elements are needed to support family planning integration into UHC, thereby reducing health system barriers and ensuring equitable access to quality family planning services for all population groups.

Family planning plays a critical role in achieving Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3, which aims to ensure that quality, affordable health care is available for individuals to lead productive and fulfilling lives. To reach SDG 3 and its targets, family planning must be considered in national and global actions to achieve universal health coverage (UHC) including health sector reform that increases access to quality essential services and reduces out-of-pocket spending.
This guide shares a framework for understanding the legal, regulatory, and policy elements of health financing efforts working towards UHC. The guide includes an explanation of how to identify and assess different policy elements that may either enhance or inhibit family planning integration within UHC schemes.
About Health Policy Plus
Health Policy Plus (HP+) is a seven-year cooperative agreement funded by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), beginning August 28, 2015. HP+ strengthens and advances health policy priorities at global, national, and subnational levels. The project aims to improve the enabling environment for equitable and sustainable health services, supplies, and delivery systems through policy design, implementation, and financing.
Health Policy Plus (2020)
Guide for Examining the Legal, Regulatory, and Policy Environment for Family Planning Inclusion in Universal Health Coverage Schemes

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Youth ages 15–24 have higher rates of contraceptive discontinuation than older women. It is critical to examine the drivers of contraceptive discontinuation that may inhibit young people from achieving their reproductive intentions. This policy brief includes seven policy actions countries can take to address obstacles to contraceptive continuation for young people.

To align with health sector and development goals, family planning programs are often structured in ways that intrinsically emphasize the initiation of new users. Elevating program goals and monitoring systems that also focus on current users will enhance the quality and reach of family planning programs. Launched by PRB in 2021, this policy brief describes patterns of contraceptive discontinuation among youth and summarizes the evidence on the drivers of discontinuation. It outlines policy and program strategies that may address obstacles to contraceptive continuation among young women who wish to prevent, delay, or space pregnancies. A virtual policy dialogue addressing youth contraceptive discontinuation in West Africa in spring 2021 used the brief’s recommendations to assess the favorability of the policy environment for sustained contraceptive use in five Ouagadougou Partnership countries, highlighting that many of these practices are not currently reflected in country policies. An associated slide deck is freely available as an advocacy tool for youth leaders. The policy brief and slide deck are available in English and French.
About Population Reference Bureau (PRB)
PRB is a nonpartisan research organization focused on improving the health and well-being of people globally through evidence-based policies and practices.
Population Reference Bureau (2021)
Best Practices in Sustaining Youth Contraceptive Use

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
The evidence summary and policy brief recommend actions needed to minimize service disruptions that are applicable beyond the COVID-19 pandemic.

Since March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic has posed a threat to sustained access to and use of essential health services. The limited data available indicate that disruptions in services have varied across and within countries, by service type, and across different waves of the pandemic.
This rapid evidence summary, developed by the MOMENTUM Knowledge Accelerator project in February 2021, reviews emerging evidence of the effects of the pandemic on provision and demand of maternal, newborn, and child health and nutrition; family planning; and reproductive health services and highlights strategies that can mitigate disruptions. The accompanying policy brief offers recommendations to maximize the impact of response efforts and strengthen the evidence base to inform current and future efforts. While many of the recommendations focus on service delivery, several highlight policy approaches to guide program implementation during the pandemic.
About MOMENTUM Knowledge Accelerator
MOMENTUM Knowledge Accelerator (MKA) is a USAID-funded project implemented by PRB, JSI Research & Training Institute, and Ariadne Labs. MKA works with other MOMENTUM awards to develop mechanisms and tools that form the foundation of MOMENTUM’s collaboration, learning, and adaptation practices and share the collective story of MOMENTUM’s contributions to help countries assist mothers, newborns, and children reach their full potential.
MOMENTUM Knowledge Accelerator (2020)
Effects of COVID-19 on Essential MNCHN/FP/RH Care and the Strategies and Adaptations Emerging in Response: Rapid Evidence Summary

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Policy environments support health systems that need to be equipped to meet the diverse needs of adolescents. This webinar explores some impactful approaches to systems change from different contexts.

On March 16, 2021, the NextGen RH CoP, Knowledge SUCCESS, E2A, FP2030, and IBP hosted a webinar, “Adolescent Family Planning and Sexual and Reproductive Health: A Health Systems Perspective,” that explored the updated High Impact Practice (HIP) brief on adolescent responsive contraceptive services.
This web article provides a helpful recap of the March 2021 webinar by summarizing themes explored during the webinar, including existing challenges to implementing a health systems approach and how to meaningfully engage adolescents and youth in accountability mechanisms.
About Knowledge SUCCESS
Knowledge SUCCESS (Strengthening Use, Capacity, Collaboration, Exchange, Synthesis, and Sharing) is a five-year global project led by a consortium of partners and funded by USAID’s Office of Population and Reproductive Health to support learning, and create opportunities for collaboration and knowledge exchange, within the family planning and reproductive health community.
Knowledge SUCCESS (2021)
Adolescent Responsive Health Systems Recap

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Self-care allows individuals and communities to become agents of their own health and should be embedded within strong health systems. This resource highlights policy advocacy opportunities related to key self-care intervention areas, including aspects of the policy environment that may need to be addressed in each intervention area.

The World Health Organization defines self-care as “the ability for individuals, families and communities to promote, maintain health, prevent disease and cope with illness with or without the support of a healthcare provider.” While the concept is not new, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the need to expand self-care options for family planning and reproductive health. However, while self-care can enhance autonomy and access to FP/RH services, it should not replace the need for a robust health system.
The tool is intended to help advocates identify the most strategic entry points in making progress on self-care in their countries and communities. The opportunities fall under five categories—diagnostics; drugs and devices; digital health; data and evidence; and demand, empowerment, and community engagement. Each category highlights examples, systems issues, and resources to inform context-specific advocacy initiatives, including those that strengthen a supportive policy environment for self-care.
About Advance Family Planning
Advance Family Planning (AFP) aims to increase financial investment and political commitment needed to enable all women and girls, regardless of where they live, access to quality, voluntary family planning. Based in the Population, Family and Reproductive Health Department of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and led by the Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health, AFP and its partners advocate expanding access to lifesaving contraceptive information, services, and supplies.
Advance Family Planning (2021)
Advocacy Entry Points for Self-Care in Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
This resource presents a policy framework for male engagement strategies and examples of how the framework can be applied to strengthen the enabling policy environment for family planning. Without a family planning policy environment that considers men and young boys as family planning users, change-makers, and supportive partners, the environment is not inclusive and harmful gender norms remain stagnant.

Men and boys may perceive that health facilities are not male-friendly, may feel uncomfortable discussing fertility preferences and contraceptive methods with their partners, or may be influenced by norms that say family planning is the woman’s responsibility. Given these realities, engaging men and boys is key to achieving family planning equity and shifting unequal gender and power dynamics. Male engagement improves not only women’s and girls’ health and wellbeing, but also the health of men and their children.
The HP+ project interviewed global experts in male engagement and FP to collect best practices and new research on male engagement in family planning and reproductive health. The framework is organized around men’s and boys’ three overlapping roles in family planning: as contraceptive users, as supportive partners for FP, and as agents of change. The nine-page brief includes 27 policy provisions that influence men’s and boys’ participation in FP and seven principles for male engagement.
About Health Policy Plus (HP+)
HP+ is a USAID-funded project that aims to strengthen and advance health policy priorities at global, national, and subnational levels. The project is a partnership between Palladium, Avenir Health, Futures Group Global Outreach, Plan International USA, Population Reference Bureau, RTI International, the White Ribbon Alliance for Safe Motherhood, and ThinkWell.
Health Policy Plus (2021)
A Policy Framework for Engaging Men and Boys in Family Planning







































Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details

Details

Details
Details
Details

Details
Details
Details

Details
Details
Details
Details

Details




Get The Resource
Why is it essential?
Task sharing supports contraceptive access and use by safely expanding tasks and procedures that are usually performed by higher-level medical personnel to lower- and mid-level health care professionals. This study demonstrates that, despite the five study countries being at different stages in terms of promotion and implementation of task sharing policies, they have some achievements and challenges in common. After analyzing the existing achievements and challenges, policymakers can shape policy environments to actively promote comprehensive task-sharing implementation and scale-up within family planning programs.

This study was conceptualized by Leopold Ouedraogo of the Reproductive, Maternal Health and Ageing Team; World Health Organization; and the Regional Office for Africa and implemented and published with nine co-authors (see publication for full list) and funding from the WHO Regional Office for Africa.
The study reviews evidence from various task-sharing policies and documents to explore implementation dynamics in five sub-Saharan African countries: Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire, Ethiopia, Ghana, and Nigeria. The study generates evidence on what countries can do to build on task-sharing program successes and tackle challenges. The authors summarize findings on the country background, describe existing task-sharing intervention packages, quantify midterm program impact, analyze system-level enablers and barriers, and suggest ways forward.
About BMC
BMC has an evolving portfolio of high-quality peer-reviewed journals, including Reproductive Health, which is available as an open-access publication. Reproductive Health has a particular focus on the global impact of changes in reproductive health and encourages submissions from researchers based in low- and middle-income countries.
BMC (2021)
A Rapid Review of Task-Sharing Policies

Get The Resource
Why is it essential?

Resources are grouped into four categories:




Measurement and Assessment Tools
Influencing Policy Environments
Population Reference Bureau (2018)

Influencing Policy Environments
Advance Family Planning (2017)

Influencing Policy Environments

Guttmacher Institute (2020)
Influencing Policy Environments
Influencing Policy Environments

Influencing Policy Environments

Policy Environment Overviews

Policy Resources on Key Topics
Policy Resources on Key Topics


Policy Resources on Key Topics

Policy Resources on Key Topics
Policy Resources on Key Topics
Policy Resources on Key Topics
Measurement and Asssessment Tools
Influencing Policy Environments
Policy Environment Overview
Policy Resources on Key Topics















Guttmacher Institute (2020)








Examining the Legal, Regulatory, and Policy Environment for FP
Health Policy Plus (2020)



Policy Environment Overviews
Family Planning High Impact Practices
The High Impact Practices Partnership (2019)

Health Policy Plus (2021)

Policy Framework for Engaging Men and Boys in Family Planning
Influencing Policy Environments


Men and boys may perceive that health facilities are not male-friendly, may feel uncomfortable discussing fertility preferences and contraceptive methods with their partners, or may be influenced by norms that say family planning is the woman’s responsibility. Given these realities, engaging men and boys is key to achieving family planning equity and shifting unequal gender and power dynamics. Male engagement improves not only women’s and girls’ health and wellbeing, but also the health of men and their children.
The HP+ project interviewed global experts in male engagement and FP to collect best practices and new research on male engagement in family planning and reproductive health. The framework is organized around men’s and boys’ three overlapping roles in family planning: as contraceptive users, as supportive partners for FP, and as agents of change. The nine-page brief includes 27 policy provisions that influence men’s and boys’ participation in FP and seven principles for male engagement.
About Health Policy Plus (HP+)
HP+ is a USAID-funded project that aims to strengthen and advance health policy priorities at global, national, and subnational levels. The project is a partnership between Palladium, Avenir Health, Futures Group Global Outreach, Plan International USA, Population Reference Bureau, RTI International, the White Ribbon Alliance for Safe Motherhood, and ThinkWell.
Health Policy Plus (2021)
A Policy Framework for Engaging Men and Boys in Family Planning
This resource presents a policy framework for male engagement strategies and examples of how the framework can be applied to strengthen the enabling policy environment for family planning. Without a family planning policy environment that considers men and young boys as family planning users, change-makers, and supportive partners, the environment is not inclusive and harmful gender norms remain stagnant.


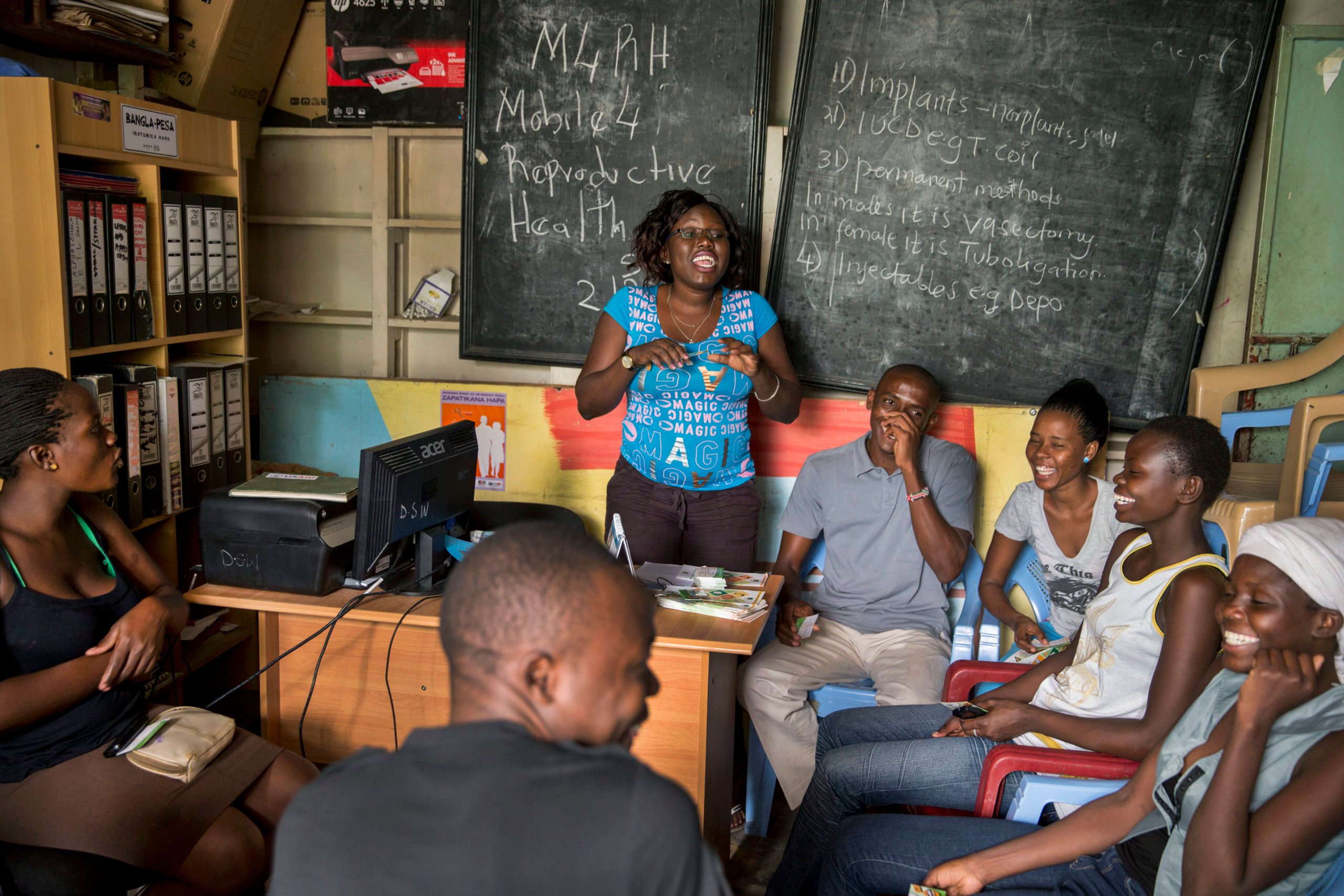









Data for Impact (2017)