ज्ञान व्यवस्थापन भनेको के हो?

ज्ञान व्यवस्थापन भनेको के हो?
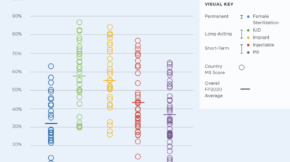
ज्ञान व्यवस्थापन (KM) को व्यवस्थित प्रक्रिया हो ज्ञान सङ्कलन र क्युरेटिङ, र मानिसहरूलाई यसमा जोड्दै र एक अर्कालाई, त्यसैले तिनीहरूले सक्छन् थप काम प्रभावकारी र कुशलतापूर्वक।
ज्ञान उच्च प्रदर्शन गर्ने स्वास्थ्य प्रणाली, सफल नीतिहरू, र राष्ट्रिय र क्षेत्रीय स्वास्थ्य लक्ष्यहरूको उपलब्धिको आधार हो। ज्ञान management has a big role to play, by encouraging continuous learning and sharing—and the application of that knowledge to services—leading to health systems that are responsive to patient and population needs.
In practice, knowledge management can take many forms. It includes activities that:
- help information flow between people, organizations, and countries so that they can share experiences and expertise,
- present information in ways that are easy for people to access, understand and apply to their context,
- nurture lasting practices of learning and sharing that are authentic to where people are.
जब विश्वव्यापी स्वास्थ्य कार्यबल सदस्यहरूले आफूलाई थाहा भएको कुरा साझा गर्छन्, र उनीहरूलाई आवश्यक पर्ने कुराहरू फेला पार्न सक्छन्, कार्यक्रमहरू उनीहरूको पूर्ण क्षमतामा पुग्न र महँगो गल्तीहरू दोहोर्याउनबाट बच्न सक्षम हुन्छन्। यसको अर्थ व्यक्ति, समुदाय र स्वास्थ्य प्रणालीका लागि राम्रो परिणाम हो।
What Does Knowledge Management Look Like in Practice?
Knowledge management can take on different forms depending on people’s needs and the challenges you’re trying to solve.
- मानिसहरूलाई सँगै ल्याउँदै सोध्नु questions and elicit tacit knowledge — or the know-how in people’s heads
- ज्ञान प्रदान गर्दै (वा बताउँदै यो) मानिसहरूको परिभाषित समूहहरूमा
- प्रकाशन र खोज्दै स्पष्ट ज्ञान साझा गर्न र मानिसहरूलाई आवश्यक पर्ने जानकारी तान्न अनुमति दिने दृष्टिकोणहरू
When implemented successfully, knowledge management has lasting impact. Resources are optimized when countries and partners can practice evidence-based decision-making, learning, and adaptation. Public health programs that often have ambitious goals, but possess limited time, money, and human resources to execute the work, can rapidly learn what works and what does not and adapt their work.

ज्ञान सङ्कलन र व्यवस्थित गर्ने:
मानिसहरूलाई एकअर्कासँग र ज्ञानमा जोड्ने:
KM को लागि क्षमता र स्रोतहरू सुदृढीकरण:
हामी एशिया र पूर्वी र पश्चिम अफ्रिकामा काम गर्ने FP/RH पेशेवरहरूका लागि क्षेत्रीय KM कार्यशालाहरू पनि आयोजना गर्छौं।