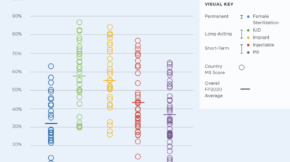
Qu'est-ce que la gestion des connaissances ?

Qu'est-ce que la gestion des connaissances ?
La gestion des connaissances (KM) est le processus systématique de collecter et conserver les connaissances, et y connecter les gens et l'un à l'autre, afin qu'ils puissent travailler plus efficacement et avec efficience.
La connaissance est le fondement de systèmes de santé performants, de politiques efficaces et de la réalisation d'objectifs de santé nationaux et régionaux. Connaissances management has a big role to play, by encouraging continuous learning and sharing—and the application of that knowledge to services—leading to health systems that are responsive to patient and population needs.
In practice, knowledge management can take many forms. It includes activities that:
- help information flow between people, organizations, and countries so that they can share experiences and expertise,
- present information in ways that are easy for people to access, understand and apply to their context,
- nurture lasting practices of learning and sharing that are authentic to where people are.
Lorsque les professionnels de santé du monde entier partagent leurs connaissances et parviennent à trouver ce dont ils ont besoin, les programmes peuvent atteindre leur plein potentiel et éviter de répéter des erreurs coûteuses. Cela se traduit par de meilleurs résultats pour les individus, les communautés et les systèmes de santé.
What Does Knowledge Management Look Like in Practice?
Knowledge management can take on different forms depending on people’s needs and the challenges you’re trying to solve.
- Rassembler les gens pour interroger questions and elicit tacit knowledge — or the know-how in people’s heads
- Transmettre des connaissances (ou révélateur il) à des groupes définis de personnes
- Édition et recherche des approches pour partager des connaissances explicites et permettre aux gens d'extraire les informations dont ils ont besoin, quand ils en ont besoin
When implemented successfully, knowledge management has lasting impact. Resources are optimized when countries and partners can practice evidence-based decision-making, learning, and adaptation. Public health programs that often have ambitious goals, but possess limited time, money, and human resources to execute the work, can rapidly learn what works and what does not and adapt their work.

Collecter et organiser les connaissances :
Renforcement des capacités et des ressources pour la gestion des connaissances :
Nous organisons également des ateliers régionaux de gestion des connaissances pour les professionnels de la PF/SR travaillant en Asie et en Afrique de l’Est et de l’Ouest.